| Table of Contents |  |
|
Case Report
| ||||||
| A giant pelvic epidermoid cyst with malignant transformation to squamous cell carcinoma | ||||||
| Ryo Fujita1, Shigeo Takebayashi2, Zenjiro Sekikawa3, Izumi Torimoto4 | ||||||
|
1MD, Attending Physician, Diagnostic Radiology, Yokohama City University Medical Center, Yokohama, Japan.
2MD, Chief and Professor, Diagnostic Radiology, Yokohama City University Medical Center, Yokohama, Japan. 3MD, Assistant Professor, Diagnostic Radiology, Yokohama City University Medical Center, Yokohama, Japan. 4MS, Postgraduate Student, Radiology.Yokohama City University Graduate School of Medicine, Yokohama, Japan. | ||||||
| ||||||
|
[HTML Abstract]
[PDF Full Text]
[Print This Article]
[Similar article in Pumed] [Similar article in Google Scholar] |
| How to cite this article |
| Fujita R, Takebayashi S, Sekikawa Z, Torimoto I. A giant pelvic epidermoid cyst with malignant transformation to squamous cell carcinoma. Edorium J Radiol 2015;1:1–5. |
|
Abstract
|
|
Introduction:
We report a rare case of pelvic epidermoid cyst with malignant transformation to squamous cell carcinoma.
Case Report: A 48-year-old male who had difficulties of both urination and defecation. Multidetector computed tomography (MDCT) revealed a 12-cm cystic mass with a contrast enhanced mural tumor in the presacral area extending to the left ischioanal space. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan showed that the mural tumor with gadolinium-diethlene triamine penta acetic acid (Gd-DTPA) contrast enhancement extended both the interior and over the wall of the cystic mass. A hypermetabolic activity with 10.7 of maximum standardized uptake value (SUV max) was limited to the mural tumor in the left anterior superior wall of the mass, but no increased activity in other portion of the wall. Unknown origin malignant cell was obtained percutaneous core biopsy under ultrasound guidance. Anaplastic malignant cell carcinoma was made on a core needle biopsy on surgical exploration after percutaneous core biopsy under ultrasound guidance demonstrating unknown origin malignant cell. The patient underwent four courses of chemotherapy using paclitaxel. Follow-up FDG-PET/CT demonstrated decreased SUV max of the mural tumor was 3.7 that is greater than normal upper limit. Subsequently, the resection of both the tumor and the rectum were performed. Pathological examination demonstrated squamous cell carcinoma in the epidermoid cyst. Conclusion: A pelvic epidermoid cyst with malignant transformation to must be considered in the differential diagnosis of a pelvic cystic tumor although it is extremely rare. | |
|
Keywords:
Epidermoid cyst, Pelvic cyst, Presacral cyst, Squamous cell carcinoma
| |
|
Introduction
| ||||||
|
An epidermoid cyst which is a benign congenital lesion develops from a remnant of ectodermal tissue misplaced during embryogenesis [1]. It can develop in any part of the human body, but occurs rarely in the pelvis. To date, we have found approximately 70 cases of pelvic epidermoid cysts in English literature [1] [2] [3] [4] [5]. Histologically, it has a thin wall lined by stratified squamous epithelium, surrounding a mixture of desquamated debris, cholesterol, keratin, and water [3]. Malignant transformation of an epidermoid cyst to squamous cell carcinoma has been described in the brain, liver, and skin, but scanty in the pelvis [6] [7] [8]. In this article, we report a large pelvic epidermoid cyst occurring malignant transformation to squamous cell carcinoma and describe its radiological imaging findings. | ||||||
|
Case Report
| ||||||
|
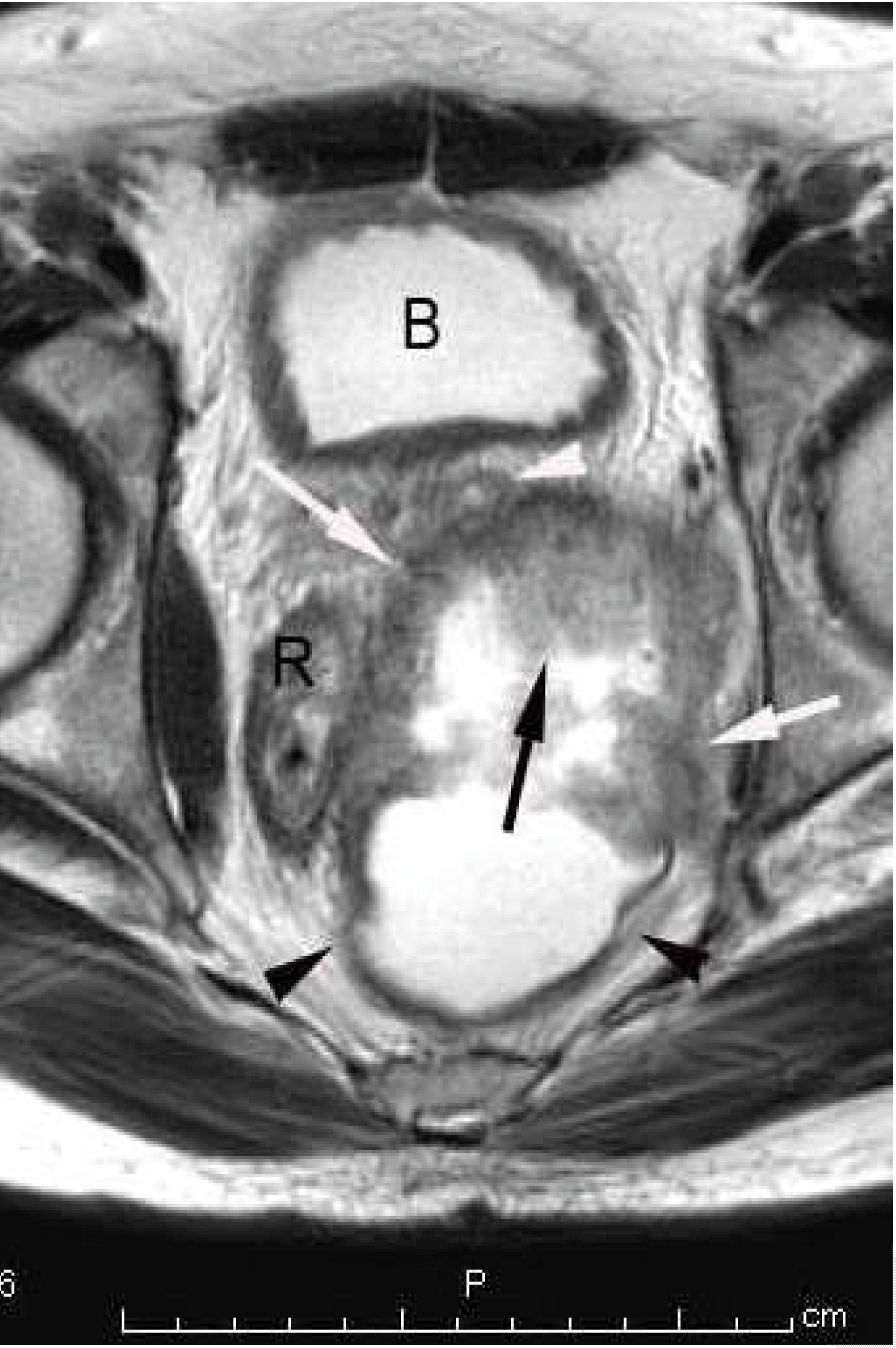
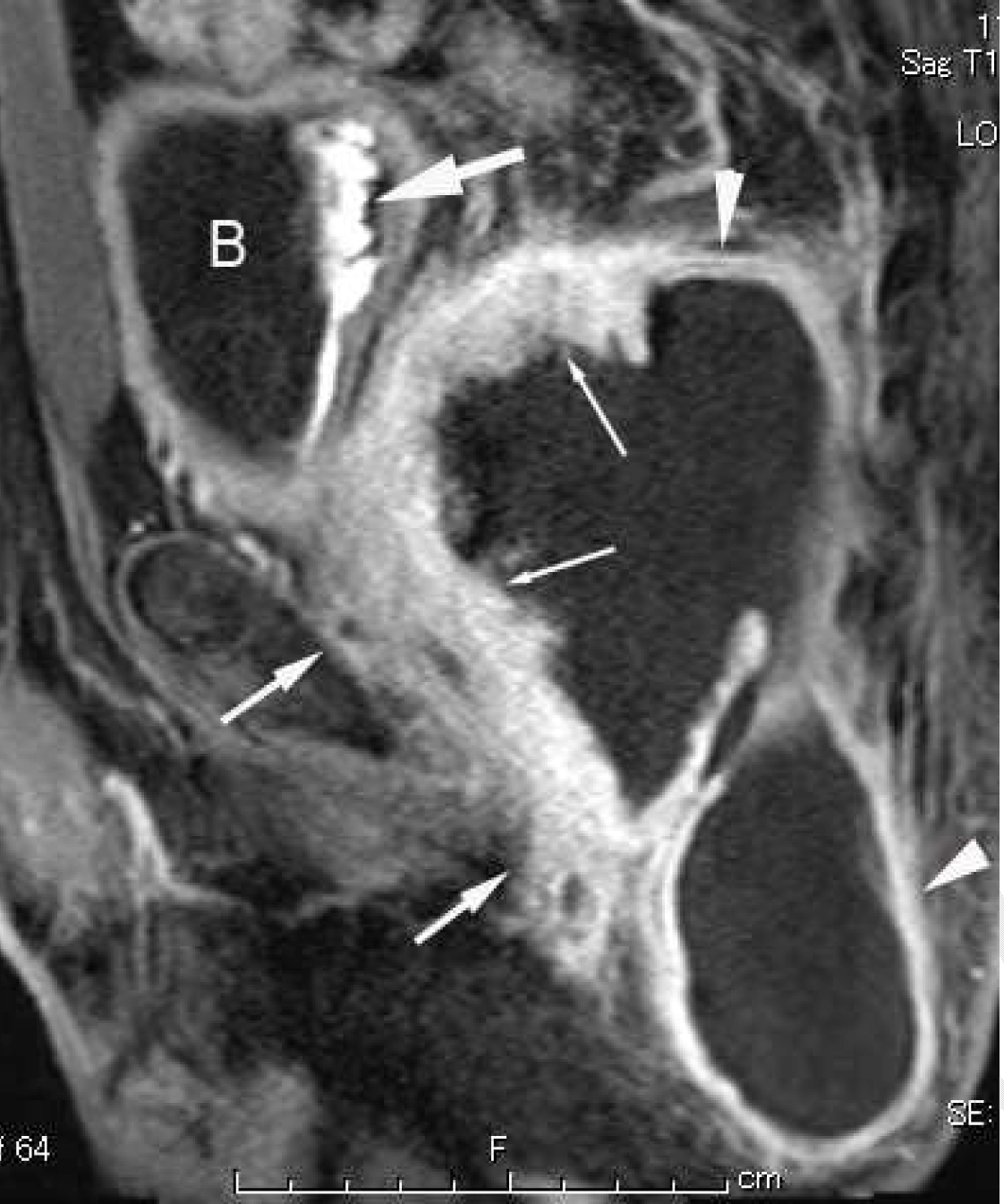
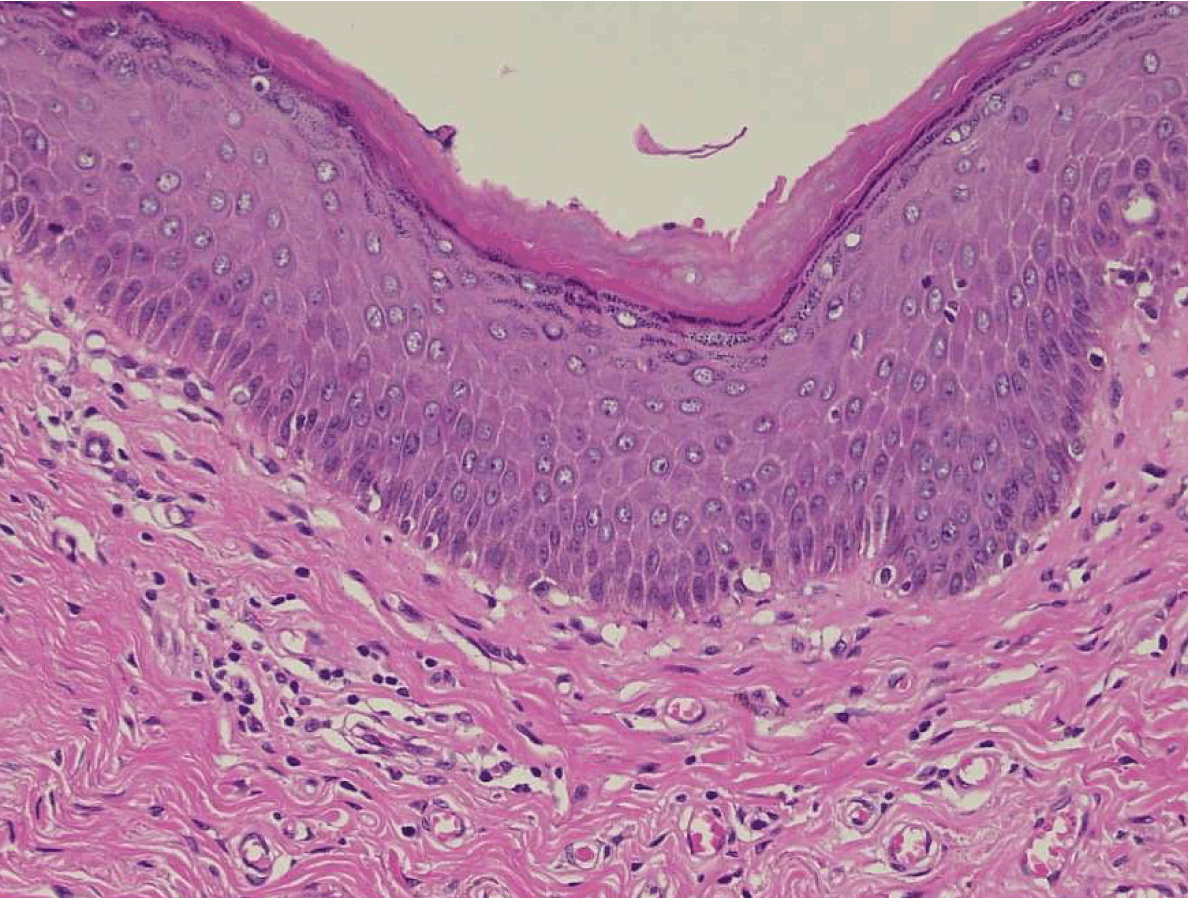
A 48-year-old male was referred to the department of the surgery in our hospital because he had pain and swelling in the left side of the buttocks. He had a history of difficulties of both urination and defecation since one month before. No abnormalities were shown in complete blood counts, chemistry proiles, routine laboratory examinations and serum levels of both carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and carbohydrate antigen (CA)-19-9. The lower rectum had an extrinsic stenosis with an intact mucosa on colonoscopy. Abdominal sonography demonstrated a 12-cm cystic mass with an echogenic mural tumor in the pelvis. Multidetector computed tomography (MDCT) revealed that the cystic mass that was located in the presacral space extending to the left ischioanal space had a mural tumor with mildly contrast enhancement. Magnetic resonance imaging (Magnetom Avanto 1.5 tesla, Siemens Medical System, Germany) showed that the mural tumor with low signal intensity on T1-weighted images and intermediate intensity on T2-weighted images (Figure 1) had gadolinium-diethlene triamine penta acetic acid (Gd-DTPA) contrast enhancement and extended both the interior and over the wall of the cystic mass (Figure 2). To evaluate malignancy in the lesion, F-18-fluorodeoxy glucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET/ CT) was performed. A hypermetabolic activity with 10.7 of maximum standardized uptake value (SUV max) was limited to the mural tumor in the left anterior wall of the mass (Figure 3), but no increased activity in other mural tumors. Percutaneous core biopsy under ultrasound guidance was performed to obtain histological diagnosis of the mural tumor with a hypermetabolic activity and unknown origin malignant cell was obtained. On surgical exploration, therefore, a core needle biopsy of the mural tumor instead of the resection the mass was performed because the mass was invaded to the surrounding structures including the sciatic nerve. Subsequently, a tentative diagnosis of anaplastic malignant cell carcinoma or angiosarcoma appeared as a cluster of spindle cells was made by a pathologist. The patient underwent four courses of chemotherapy using paclitaxel. Follow-up FDG-PET/ CT demonstrated decreased with 3.7 of SUV max in the mural tumor in the left anterior wall (Figure 4). Subsequently, the resection of both the tumor and rectum was accomplished. Final diagnosis of epidermoid cyst with malignant transformation to squamous cell carcinoma was made on microscopic examinations (Figure 5). The postoperative course was uneventful, but local recurrence occurred at a six-month follow-up after the surgery. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
|
| ||||||
|
| ||||||
|
| ||||||
| ||||||
|
Discussion
| ||||||
|
The presacral or pararectal space is a potential site for various types of cysts and tumors because it consists of many types of embryonic tissue. Cystic masses in the space are classified into two groups: (i) developmental cysts including epidermoid, dermoid, enteric, and neurenteric cysts and (ii) teratomas [4]. In patients with the cystic mass as our present case, symptoms of constipation, pain or dysuria may occur resulting from local mass effect although the major complications of these masses are infection with fistula and hemorrhage [7]. Chronic in?ammation of the cyst is thought to have a stimulating effect on the cystic epithelium to develop malignant change [9]. Glasgow et al. showed that the accuracy of diagnosis of pararectal cystic tumor was less than 30% and that various imaging modalities were not useful in establishing a definitive diagnosis [8]. Surgical excision is thought to be mandatory to establish the diagnosis and avert complications. The diagnosis of the cystic mass on radiological imaging is quite challenging because epidermoid cyst is shown as non-specific cystic mass which is low density mass on MDCT and hypointensity on T1-weighted MR image and homogeneous hyperintensity on T2-weighted MR image. But Halefoglu et al. had reported that a large presacral epidermoid cyst had hyperintensity on a diffusion weighted image although the sequence was not obtained in this present case [5]. Furthermore, preoperative diagnosis of epidermoid cyst with malignant transformation is difficult as this present case because pelvic epidermoid cyst with malignant transformations is extremely rare. To our knowledge, there is only one case of pelvic epidermoid cysts with malignant transformations in English literatures [2]. The differential diagnosis in pararectal cystic tumors includes gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) with large cystic degeneration, ovarian tumors, neurogenic tumors such as paragangliomas and schwannomas. The GIST may easily grow in a pedunculated and exophytic pattern although only about 9% of all GISTs originate in the rectum [9]. Central necrosis can be caused by recurrent congestion, hemorrhage when the tumors are twisted or grow faster than the capacity of blood supply. The solid portion of GIST is usually hyperintense on T2-weighted MRI [9], indicative of dense cellularity. But T2-hypo- or intermediate intensity was also in the solid portion of a cystic pararectal GIST. Epidermoid cysts are often mimicking ovary cysts at preoperative imaging in women [4]. Neurogenic tumors, especially schwannomas often have cystic changes. T2-weighted MRI scan may differentiate peripheral schwannomas with hyperintensity from epidermoid cyst with malignant transformations appearing as intermediate signal. Contrast enhancement in the mural lesion in MDCT or MRI scan suggests malignant lesion in pelvic cyst. FDG-PET/ CT is potentially able to depict malignant transformation. In this present case, however, hypermetabolic activity was not demonstrated in squamous cell carcinoma in the cystic wall but the mural mass with anaplastic squamous cell carcinoma.Ultrasound or CT-guided core-needle biopsy proved either inconclusive or inaccurate in the diagnosis of schwannomas when compared with the histology obtained following surgical excision [8]. In the diagnosis of the disease, complete resection of the cyst is mandatory. Combined laparoscopic and perineal surgical approach is suggested to be appropriate in management of giant pelvic cystic tumors, because the major advantage being minimal damage to vital organs, complete resection, and rapid recovery [4]. We propose a following imaging strategy to evaluate presacral or pararectal cystic masses associated with tumors. MRI scan is superior to MDCT and sonography in the evaluation of mural tumor extending over the wall of the cystic mass. FDG-PET/CT is useful in the detection of a high-grade malignancy such as anaplastic cell carcinoma. But it may fail to detect a low-grade malignancy of squamous cell carcinoma [10]. | ||||||
|
Conclusion
| ||||||
|
In this report, we present a case of a presacral epidermoid cyst with malignant transformation to squamous cell carcinoma. Although such a case is quite rare, its importance lies in that it must be differentiated from the more common other cysts in the pelvis. | ||||||
|
References
| ||||||
| ||||||
|
[HTML Abstract]
[PDF Full Text]
|
|
Author Contributions
Ryo Fujita – Substantial contributions to conception and design, Acquisition of data, Analysis and interpretation of data, Drafting the article, Critical revision of the article, Final approval of the version to be published Shigeo Takebayashi – Substantial contributions to conception and design, Acquisition of data, Analysis and interpretation of data, Drafting the article, Critical revision of the article, Final approval of the version to be published Zenjiro Sekikawa – Substantial contributions to conception and design, Acquisition of data, Analysis and interpretation of data, Drafting the article, Critical revision of the article, Final approval of the version to be published Izumi Torimoto – Substantial contributions to conception and design, Acquisition of data, Analysis and interpretation of data, Drafting the article, Critical revision of the article, Final approval of the version to be published |
|
Guarantor of submission
The corresponding author is the guarantor of submission. |
|
Source of support
None |
|
Conflict of interest
Authors declare no conflict of interest. |
|
Copyright
© 2015 Ryo Fujita et al. This article is distributed under the terms of Creative Commons Attribution License which permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium provided the original author(s) and original publisher are properly credited. Please see the copyright policy on the journal website for more information. |
|
|